Panxing New Metal Technology White Paper
Bulk non-magnetic amorphous steel has broad potential application prospects in mechanical structural materials, tool materials, corrosion-resistant materials, biomedical materials, and sports equipment materials.
Since P.Duwez et al. prepared amorphous alloy thin strips by melting and quenching method in 1960, amorphous alloys have officially entered the field of materials, and many new systems and excellent properties have been continuously discovered. Especially in the past two decades, breakthroughs have been made in the preparation, development and research of bulk amorphous alloys. Among them, Fe-based amorphous alloys have high strength, high corrosion resistance, excellent soft magnetic properties and strong The price advantage stands out from the total polyamorphous alloys and attracts much attention.
The concept of "amorphous steel" alloy was first proposed by S. Joseph Poon et al. in 2003. The research results found that the magnetic transition temperature of Fe-based amorphous alloy with a diameter of 12 mm is much lower than room temperature, that is to say, at room temperature, this crystalline alloy has a magnetic transition temperature. It exhibits non-magnetic properties, so the concept of "Amorphous nonferromagnetic steel alloys" is proposed. In this research result, the first Fe48Cr15Mo14Er2C15B6 amorphous steel composition with a maximum forming size of 12mm was born. Coincidentally, in 2004, Z.P.Lu et al. proposed the concept of "Structural amorphous steel" structural amorphous steel. Therefore, the Fe-based bulk amorphous alloy that is non-magnetic at room temperature and aimed at structural engineering applications is called non-magnetic amorphous steel, abbreviated as non-magnetic amorphous steel. Amorphous steel.
Currently reported amorphous steels mainly include Fe-Mo-(B,C) series, Fe-Zr-B series, Fe-Cr-Co-Mo-C-B series and Fe-Mn-Cr-Mo-(Y,Ln) series -C-B series, the amorphous steel containing Er, Y, Dy elements has better forming ability, and t
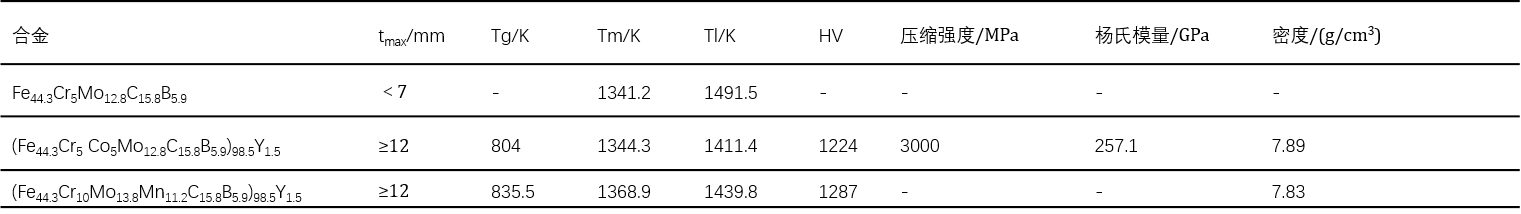
B. The amount of metalloid and metalloids reduces the preparation cost, thereby better pushing the amorphous steel to practical engineering applications.
Amorphous steel composition design ideas:
1) To suppress the magnetic effect, Mn and a small amount of Cr are commonly used as additive elements to suppress ferromagnetism;
2) Reduce Tl to obtain high Trg, add non-metallic elements, Mn and refractory metals Zr, Nb, Mo to reduce Tl, but adding Cr will increase Tl;
3) To increase Tg, the addition of refractory metal increases the elastic modulus and enhances the stability of the amorphous structure, thereby increasing the Tg;
4) To formulate the alloy composition, consider the ratio of atoms of three different sizes, namely Fe (Mn) atoms, non-metallic small atoms and refractory metal large atoms, and the optimal large atom content (mass fraction) is estimated to be 10. Such an atomic size distribution of about % can further strengthen the amorphous structure, because in the atoms constituting the framework, the refractory large atoms have high coordination numbers, and the non-metallic small atoms occupy the interstitial positions. This structure can be more effective. It interacts with the main constituent Fe atoms.
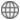
Although the above alloy components have high glass-forming ability, they must be prepared with high-purity elements under high vacuum degree, which greatly increases the production cost and processing complexity. In response to this problem, Lv Zhaoping's team from the State Key Laboratory of New Metal Materials, University of Science and Technology Beijing, in cooperation with Gyeongbuk National University in South Korea, successfully prepared industrial pig iron, industrial ferroalloy and commercial gradient pure elements by arc melting and copper mold suction casting. The critical dimension is 7mm industrial grade Fe69.9C7.1Si3.3B5.5P8.7Al2.0Mo2.5Co1.0 amorphous steel, the alloy exhibits strong glass forming ability and thermal stability, and has a low liquidus.
Technical Research-Alloy.jpg
Although the development and research of non-magnetic amorphous steel have problems such as composition sensitivity, serious influence of oxide impurities, harsh synthesis conditions and low Fe content, it does not affect its huge and gratifying application prospects. Compared with the traditional steel with crystalline structure, bulk amorphous steel has many outstanding excellent properties. The yield strength of bulk amorphous steel is two to three times higher than that of conventional high-strength steels, and the elastic modulus is comparable to that of super austenitic steel alloys.
In addition, non-ferromagnetic properties at room temperature, lower raw material cost, better corrosion resistance, higher thermal stability (glass transition temperature close to or higher than 900 K) and many other excellent properties make the bulk Non-magnetic amorphous steel is widely regarded as a new structural material. Large pieces of non-magnetic amorphous steel can be used as the surface protection of the hull. Its non-magnetic, strong seawater corrosion resistance and high strength make the non-magnetic amorphous steel hull incomparable with traditional crystalline steel in terms of service life. Advantage. At the same time, the bulk non-magnetic amorphous steel has broad potential application prospects in mechanical structural materials, tool materials, corrosion-resistant materials, biomedical materials, and sports equipment materials.
references:
[1]Jun Shen,Qingjun Chen,Jianfei Sun,Hongbo Fan,Gang Wang,Exceptionally high glass-forming ability of an FeCoCrMoCBY alloy,[J],APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS 86, 151907 (2005).
[2]S.J. Pang et al.Bulk glassy Fe–Cr–Mo–C–B alloys with high corrosion resistance,[J],Corrosion Science 44 (2002) 1847–1856.
[3]Hyo Yun Jung,Su Ji Choi,Konda G. Prashanth,Mihai Stoica,Sergio Scudino,Seonghoon Yi,Uta Kühn,Do Hyang Kim,Ki Buem Kim,Jürgen Eckert. Fabrication of Fe-based bulk metallic glass by selective laser melting: A parameter study[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 86.
[4] Xie Chunxiao, Yang Yuanzheng. Research progress on the plasticity of Fe-based bulk amorphous alloys [J]. Materials Review, 2012, 26(09): 98-101.
[5] Li Hongxiang, Lv Zhaoping, Wang Shanlin, Li Chengxun. Research and application status and prospect of bulk amorphous steel alloys [A]. Chinese Mechanical Engineering Society, Chinese Mechanical Engineering Society Foundry Branch. 2009 China Foundry Week Proceedings [C] . Chinese Mechanical Engineering Society, Chinese Mechanical Engineering Society Foundry Branch: Chinese Mechanical Engineering Society Foundry Branch, 2009: 9.




 CH
CH




